The 10 Scariest Things About Glaucous Macaw
페이지 정보

본문
Glaucous Macaw
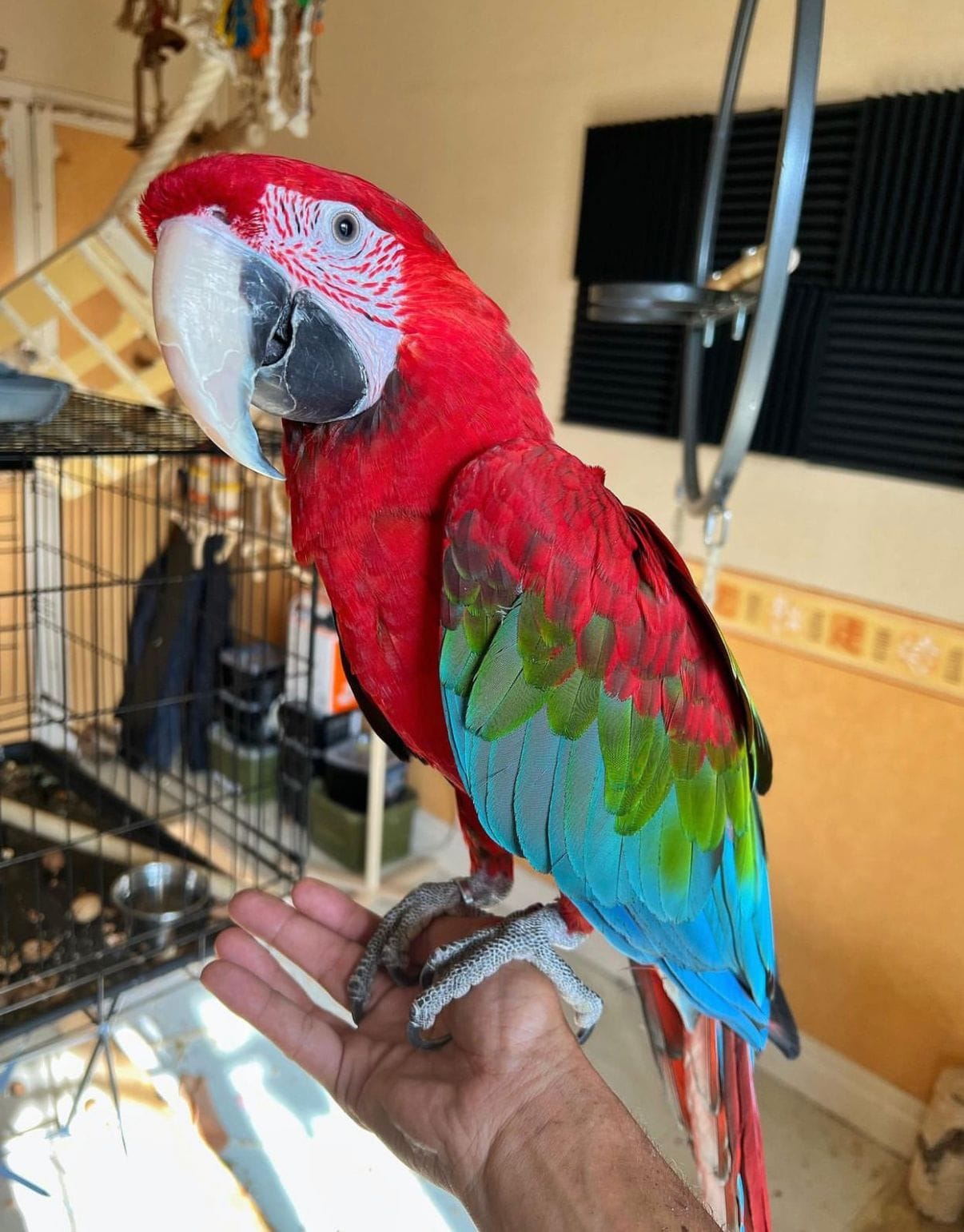 The glaucous macaw (bullard-gregory.hubstack.net) can be described as one of the rarest birds in the world. It is in danger of disappearing and may even be extinct.
The glaucous macaw (bullard-gregory.hubstack.net) can be described as one of the rarest birds in the world. It is in danger of disappearing and may even be extinct.
 This bird has been reported by aviculturists across the globe, but the latest sighting was in 1992. The alleged sighting was reported to have occurred in the southwestern region of Paraguay, near the city of Corrientes. The bird was a male.
This bird has been reported by aviculturists across the globe, but the latest sighting was in 1992. The alleged sighting was reported to have occurred in the southwestern region of Paraguay, near the city of Corrientes. The bird was a male.
Origin
The Glaucous macaw is an endangered parrot species that is native South America. This magnificent bird is characterized by the blue feather pattern and a strong beak capable of cracking open seeds and nuts. Glaucous macaws are known to form long-term monogamous couples and both parents assist in raising the chicks. The chicks are fed regurgitated food for the first couple of weeks of life before being fed solid food as the chicks grow. The parents also are a key part of teaching the young macaws how to fly and forage.
The glaucous Macaw has gone extinct, but rumors about its existence continue to spread all over the world. The glaucous Macaw is believed to have been extinct in the 1800s due to cattle grazing on yatay (Butia) palm groves, where the birds would gather their food. The glaucous Macaw is believed to have made a comeback, and is often kept with its larger cousin, Lear's macaw.
In terms of habitat, the glaucous macaw can be found in the sub-tropical forests of South America. They are typically located in areas where there are many palm trees. They are also very adaptable to various types of forested environments. These beautiful birds why are the glaceous macaw and hyancith macaw so alike also known to be extremely territorial and will protect their feeding and nesting areas from intruders.
There have been a number of reports about the glaucous macaw over the years, but they are considered to be unreliable. The most recent report of a wild event is an avicultural acquaintance of Ridgely's who claimed to have witnessed four Glaucous macaws in Califomia. This claim is untrue until it can backed up by solid evidence. The absence of any reliable data on this bird over the past century has led many experts to believe that it is extinct, yet they have always been willing to accept the possibility of survival (Vielliard 1979, Ridgely 1981a, Sick 1985, Chebez 1986a). If it does survive it is highly unlikely to reach large numbers.
Habitat
The glaucous macaw is a striking bird that is known for its size and dazzling turquoise-Lolita blue & gold macaw coloration. The long tail and wings accentuate its graceful and agile movements. The bird is a symbol of loyalty and love. Its beak, which is primarily black, has a distinct shape and allows it to break seeds and nuts. They are a significant part its diet.
The Glaucous Macaw is considered Critically Endangered by the IUCN, which notes that it is a small population and Glaucous Macaw is at a significant chance of becoming extinct. The species was once widespread, but is now only found in northern Argentina, south Paraguay and north-eastern Uruguay as well as Brazil, from Parana state to south, where it nests in cliffs along major rivers.
Although there haven't been any reliable sightings of this species since 1830 The Glaucous Macaw seemed not to be a rare species in its limited range. specimens were taken until 1860 (in Corrientes). The last known living Glaucous Macaw was seen at the Buenos Aires Zoo in 1936 and is believed to be from Brazil.
The reassessment suggests that the species is a generalist, and prefers areas of savanna that are interspersed with palm "islands" and riparian forest bands along river systems. It was a specific food source for palm fruits, especially those of the chatay or yatay palm (Butia yatay), but it was likely to also consume ripe and unripe fruits such as berries, nuts, and vegetables. It nested on steep slopes and cliffs, sometimes in tree cavities, and laid an average clutch of two eggs.
Like all parrots, this bird was social, and was probably gregarious. It could live up to 14.8 years in captivity. It was said to be a reliable breeder, reproducing year after year. The lifespan of the species in the wild was perhaps between 50 and 80 years. This species was a potent disperser of seeds and could have contributed to the success of the palm yatay in its natural habitat.
Feeding
The Glaucous Macaw (Anodorhynchus glaucus) is one of the most magnificent of all the parrot species and its presence has an immense impact in its surroundings. This large South American bird is known for its vibrant blue feathers and eyes that are yellow, as well as its distinctive teardrop-shaped lipped sleeve that covers the lower part of its beak.
Up until recently, very little was known about the diet of the Glaucous Macaw. The first references to the subject I have discovered are in two books by H.W. Bates, "The Naturalist on the Amazons" first published in 1863, detailing his 11-year stay in Brazil and later in his book "As Birds of the Brazilian Forests". Both of these are about the Hyacinthine Macaw (Anodorhynchus aureolarius) however I see no reason to think that they are not applicable to this species.
It is probable that the Glaucous severe macaw was a specialist for the consumption of palm nuts. It also ate other seeds, fruits and vegetable matter in smaller quantities. The diet of this species is likely to be affected by the clearing of forests by early colonists to cultivate and cattle ranching, as well as the destruction of the yatay palm (Butia yatay) from which it may have gotten a lot of its nutrition.
In the wild, the Glaucous Macaw was found in subtropical forests containing mountains and savannahs that were surrounded by palm trees where it nested in tree cavities, on rocky banks or the top of palm fronds. The female incubates and lays two eggs on average.
The young Glaucous Macaws are altricial, meaning they rely on their parents to look after them until they're fully grown and fly. Both females and males are extremely dedicated to their young and will continuously hunt for food and protect them from predators.
Unfortunately, the Glaucous Macaw has been eradicated from its entire previous range. The disappearance of the magnificent bird is likely to be due to the continued trapping of birds for the pet industry, as well as disturbance to habitat, particularly the massive clearing of palm yatays which may have been its primary food source. The Glaucous Macaw is classified as Critically Endangered.
Breeding
Glaucous macaws usually form long-term monogamous pairs and both parents play an active role in the raising of the young. They breed in the dry season, which is when the food supply is at its highest. Females lay a clutch of two to three eggs, which are incubated for about 28 days. After hatching, they are fed by their parents via regurgitation for the first couple of weeks of their lives. Then the young macaws begin to explore their surroundings and begin to learn to feed themselves. They also learn how to fly and forage.
Like all birds, glaucous macaws are highly social creatures. They are active during the day but sleep at night. At night they often seek refuge inside tree cavities or other nesting areas that are suitable. Their calls can be heard throughout the forest throughout the day.
The species is expected to rebound from its decline, however it is in danger of being wiped out by habitat loss, illegal trapping of the bird for pet trade, and deforestation. It is believed that there are less than 20 glaucous macaws living in the wild. The IUCN has classified the bird as "Critically endangered--possibly extinct."
The glaucous Macaw, sometimes referred to as Lear's Macaw or Melody blue spix macaw-throated Hummingbird, is distinguished by its vibrantly blue feathers. The parrot is 70 centimeters long and features a an impressive beak that is capable of breaking open nuts and seeds. This beautiful bird is native to South America, and it can be found in many habitats like grasslands, forests, dry lowland and wetland.
This magnificent bird is an emblem of South American biodiversity. Its elegant appearance, with its slender body, light build, and vibrant blue feathers. Its black and curved beak makes it easier to crack open seeds and nuts which are a large part of its diet. It is a stunning bird that is often seen in birds shows. It is also a favorite in captivity, where it could live for a lifetime.
 The glaucous macaw (bullard-gregory.hubstack.net) can be described as one of the rarest birds in the world. It is in danger of disappearing and may even be extinct.
The glaucous macaw (bullard-gregory.hubstack.net) can be described as one of the rarest birds in the world. It is in danger of disappearing and may even be extinct. This bird has been reported by aviculturists across the globe, but the latest sighting was in 1992. The alleged sighting was reported to have occurred in the southwestern region of Paraguay, near the city of Corrientes. The bird was a male.
This bird has been reported by aviculturists across the globe, but the latest sighting was in 1992. The alleged sighting was reported to have occurred in the southwestern region of Paraguay, near the city of Corrientes. The bird was a male.Origin
The Glaucous macaw is an endangered parrot species that is native South America. This magnificent bird is characterized by the blue feather pattern and a strong beak capable of cracking open seeds and nuts. Glaucous macaws are known to form long-term monogamous couples and both parents assist in raising the chicks. The chicks are fed regurgitated food for the first couple of weeks of life before being fed solid food as the chicks grow. The parents also are a key part of teaching the young macaws how to fly and forage.
The glaucous Macaw has gone extinct, but rumors about its existence continue to spread all over the world. The glaucous Macaw is believed to have been extinct in the 1800s due to cattle grazing on yatay (Butia) palm groves, where the birds would gather their food. The glaucous Macaw is believed to have made a comeback, and is often kept with its larger cousin, Lear's macaw.
In terms of habitat, the glaucous macaw can be found in the sub-tropical forests of South America. They are typically located in areas where there are many palm trees. They are also very adaptable to various types of forested environments. These beautiful birds why are the glaceous macaw and hyancith macaw so alike also known to be extremely territorial and will protect their feeding and nesting areas from intruders.
There have been a number of reports about the glaucous macaw over the years, but they are considered to be unreliable. The most recent report of a wild event is an avicultural acquaintance of Ridgely's who claimed to have witnessed four Glaucous macaws in Califomia. This claim is untrue until it can backed up by solid evidence. The absence of any reliable data on this bird over the past century has led many experts to believe that it is extinct, yet they have always been willing to accept the possibility of survival (Vielliard 1979, Ridgely 1981a, Sick 1985, Chebez 1986a). If it does survive it is highly unlikely to reach large numbers.
Habitat
The glaucous macaw is a striking bird that is known for its size and dazzling turquoise-Lolita blue & gold macaw coloration. The long tail and wings accentuate its graceful and agile movements. The bird is a symbol of loyalty and love. Its beak, which is primarily black, has a distinct shape and allows it to break seeds and nuts. They are a significant part its diet.
The Glaucous Macaw is considered Critically Endangered by the IUCN, which notes that it is a small population and Glaucous Macaw is at a significant chance of becoming extinct. The species was once widespread, but is now only found in northern Argentina, south Paraguay and north-eastern Uruguay as well as Brazil, from Parana state to south, where it nests in cliffs along major rivers.
Although there haven't been any reliable sightings of this species since 1830 The Glaucous Macaw seemed not to be a rare species in its limited range. specimens were taken until 1860 (in Corrientes). The last known living Glaucous Macaw was seen at the Buenos Aires Zoo in 1936 and is believed to be from Brazil.
The reassessment suggests that the species is a generalist, and prefers areas of savanna that are interspersed with palm "islands" and riparian forest bands along river systems. It was a specific food source for palm fruits, especially those of the chatay or yatay palm (Butia yatay), but it was likely to also consume ripe and unripe fruits such as berries, nuts, and vegetables. It nested on steep slopes and cliffs, sometimes in tree cavities, and laid an average clutch of two eggs.
Like all parrots, this bird was social, and was probably gregarious. It could live up to 14.8 years in captivity. It was said to be a reliable breeder, reproducing year after year. The lifespan of the species in the wild was perhaps between 50 and 80 years. This species was a potent disperser of seeds and could have contributed to the success of the palm yatay in its natural habitat.
Feeding
The Glaucous Macaw (Anodorhynchus glaucus) is one of the most magnificent of all the parrot species and its presence has an immense impact in its surroundings. This large South American bird is known for its vibrant blue feathers and eyes that are yellow, as well as its distinctive teardrop-shaped lipped sleeve that covers the lower part of its beak.
Up until recently, very little was known about the diet of the Glaucous Macaw. The first references to the subject I have discovered are in two books by H.W. Bates, "The Naturalist on the Amazons" first published in 1863, detailing his 11-year stay in Brazil and later in his book "As Birds of the Brazilian Forests". Both of these are about the Hyacinthine Macaw (Anodorhynchus aureolarius) however I see no reason to think that they are not applicable to this species.
It is probable that the Glaucous severe macaw was a specialist for the consumption of palm nuts. It also ate other seeds, fruits and vegetable matter in smaller quantities. The diet of this species is likely to be affected by the clearing of forests by early colonists to cultivate and cattle ranching, as well as the destruction of the yatay palm (Butia yatay) from which it may have gotten a lot of its nutrition.
In the wild, the Glaucous Macaw was found in subtropical forests containing mountains and savannahs that were surrounded by palm trees where it nested in tree cavities, on rocky banks or the top of palm fronds. The female incubates and lays two eggs on average.
The young Glaucous Macaws are altricial, meaning they rely on their parents to look after them until they're fully grown and fly. Both females and males are extremely dedicated to their young and will continuously hunt for food and protect them from predators.
Unfortunately, the Glaucous Macaw has been eradicated from its entire previous range. The disappearance of the magnificent bird is likely to be due to the continued trapping of birds for the pet industry, as well as disturbance to habitat, particularly the massive clearing of palm yatays which may have been its primary food source. The Glaucous Macaw is classified as Critically Endangered.
Breeding
Glaucous macaws usually form long-term monogamous pairs and both parents play an active role in the raising of the young. They breed in the dry season, which is when the food supply is at its highest. Females lay a clutch of two to three eggs, which are incubated for about 28 days. After hatching, they are fed by their parents via regurgitation for the first couple of weeks of their lives. Then the young macaws begin to explore their surroundings and begin to learn to feed themselves. They also learn how to fly and forage.
Like all birds, glaucous macaws are highly social creatures. They are active during the day but sleep at night. At night they often seek refuge inside tree cavities or other nesting areas that are suitable. Their calls can be heard throughout the forest throughout the day.
The species is expected to rebound from its decline, however it is in danger of being wiped out by habitat loss, illegal trapping of the bird for pet trade, and deforestation. It is believed that there are less than 20 glaucous macaws living in the wild. The IUCN has classified the bird as "Critically endangered--possibly extinct."
The glaucous Macaw, sometimes referred to as Lear's Macaw or Melody blue spix macaw-throated Hummingbird, is distinguished by its vibrantly blue feathers. The parrot is 70 centimeters long and features a an impressive beak that is capable of breaking open nuts and seeds. This beautiful bird is native to South America, and it can be found in many habitats like grasslands, forests, dry lowland and wetland.
This magnificent bird is an emblem of South American biodiversity. Its elegant appearance, with its slender body, light build, and vibrant blue feathers. Its black and curved beak makes it easier to crack open seeds and nuts which are a large part of its diet. It is a stunning bird that is often seen in birds shows. It is also a favorite in captivity, where it could live for a lifetime.
- 이전글Garage Door Repair - Simple Fixes You Are Capable Of 25.02.10
- 다음글Everything You Need To Know About Leia Blue Macaw And Red Macaw 25.02.10
댓글목록
등록된 댓글이 없습니다.